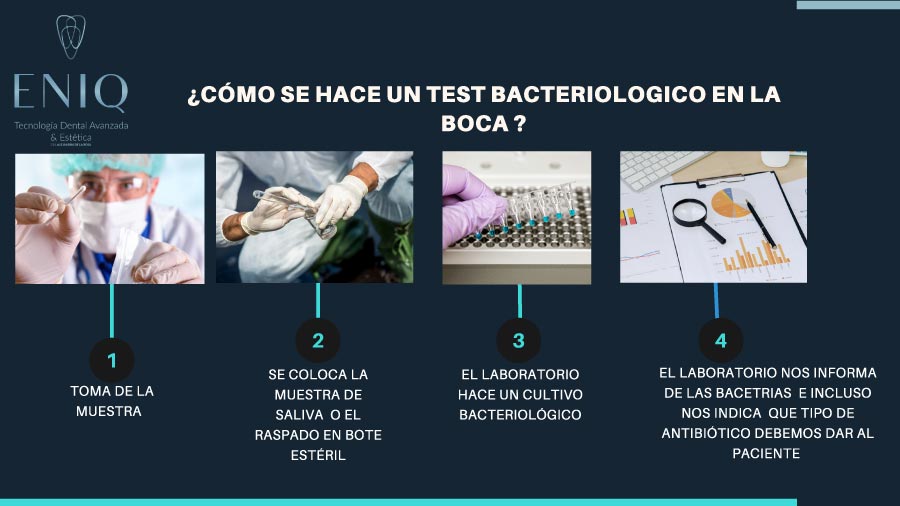
Oral Bacteriological Test
Dental bacteriological tests to identify and treat oral problems.
What is an Oral Bacteriological Test?
An oral bacteriological test, also known as an oral bacterial culture or oral microbiological analysis, is a procedure in which samples of saliva or dental plaque from the mouth are taken and cultivated in a laboratory to identify and analyze the bacteria present.
This type of test is conducted to assess the quantity and type of bacteria present in a person's mouth. It helps identify the bacteria responsible for oral diseases such as dental caries, gum diseases, and other oral infections.
The process generally involves taking a saliva sample or gently scraping the surface of the teeth or gums to collect samples of dental plaque. These samples are sent to a laboratory where they are cultivated, and bacterial growth is observed. Then, the present bacterial species are identified, and their quantity is determined.
The oral bacteriological test can be useful in specific clinical situations, such as cases of severe or recurrent periodontal diseases, to guide appropriate treatment. It provides information about an individual patient's bacterial profile and can help oral health professionals to personalize the therapeutic approach.
It is important to note that the oral bacteriological test is a specialized procedure and requires proper laboratory equipment and techniques. It should only be conducted by trained professionals in appropriate clinical and laboratory settings.
What is the Procedure for an Oral Bacteriological Test?
The procedure for conducting an oral bacteriological test at a dental clinic can vary depending on the type of test and the resources available at the clinic. Below is a general procedure that may be followed:
- Patient Preparation: Before conducting the bacteriological test, the patient may be instructed to refrain from eating, drinking, or performing any activity that could affect the sample for a certain period, usually a few hours before the procedure.
- Sample Collection: The dentist or trained personnel will take the sample from the patient's mouth. This may involve collecting saliva, gently scraping the surface of the teeth, gums, or tongue, or taking samples of dental plaque using swabs or specialized instruments. The samples will be placed in a sterile container.
- Sample Preparation and Sending: The collected samples will be placed in an appropriate transport medium to preserve the bacteria in the sample. They will then be properly labeled and sent to the laboratory for analysis.
- Bacterial Culturing: In the laboratory, the samples will be cultured in specific culture media that promote the growth of the bacteria present in the sample. Culture plates are incubated at suitable temperatures and conditions for a set period to allow bacterial growth.
- Identification and Analysis: After incubation, the bacterial colonies that have grown on the culture plates are analyzed and identified using microbiological techniques, such as microscopic observation, biochemical tests, or molecular assays. This determines the bacterial species present and their relative quantity.
- Results Reporting: Once the analysis is complete, a results report detailing the identified bacterial species and their concentrations is generated. These results are interpreted and used to guide diagnosis and appropriate treatment based on the patient's needs.
It is important to note that the exact procedure may vary depending on the dental clinic and the resources available. If you are interested in undergoing an oral bacteriological test, I recommend consulting with your trusted dentist for specific information about the procedure at their clinic.
Benefits
What Are the Benefits of Conducting a Bacteriological Test?
The primary goal of conducting a bacteriological test for periodontitis is to identify the specific bacterial species present in the periodontal pockets, as well as to assess their quantity and activity. This provides valuable information on the bacterial composition of the patient's mouth and helps determine the risk and severity of periodontal disease.
Some of the benefits and uses of a bacteriological test for periodontitis include:
- Precise Diagnosis: Helps confirm the diagnosis of periodontitis and differentiate it from other oral conditions. It allows the identification of specific bacteria associated with the disease, which can help establish an appropriate treatment plan.
- Disease Prognosis: The presence and quantity of pathogenic periodontal bacteria in the periodontal pockets can indicate the prognosis of the disease and its progression. This helps predict the response to treatment and determine the long-term risk of tooth loss.
- Treatment Guidance: Allows for the design of a personalized treatment plan, selecting more effective and targeted antimicrobial therapies, such as the use of specific antibiotics, mouthwashes, or pocket decontamination procedures, to control the bacteria causing the disease.
- Treatment Monitoring: After periodontal treatment, evaluates the effectiveness and control of periodontal bacteria. Determines whether pathogenic bacteria have decreased in quantity and if the treatment is successful.
It is important to note that the bacteriological test for periodontitis is used as a complementary tool in the diagnosis and management of the disease. It is conducted in conjunction with clinical evaluation and other periodontal examinations to obtain a complete picture of a patient's periodontal health and provide appropriate and personalized treatment.
What is the price of the bacteriological test?
Bacteriological Test
Bacterial Control
*subject to specialist assessment
Bacteriological tests range between €150 and €300, depending on how many groups of bacteria you want to study.
-
All-Inclusive
Services
All rights reserved © ENIQ Clinic 2025
Legal Notice · Privacy Policy · Cookie Policy